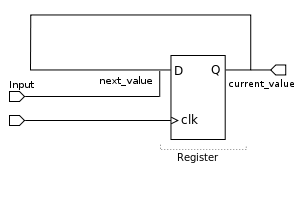
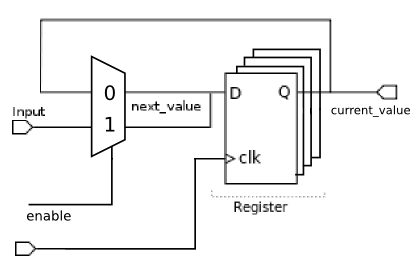
Die Vollversion:
use STD.textio.all;
library IEEE;
use IEEE.std_logic_1164.all;
package STD_LOGIC_TEXTIO is
--synopsys synthesis_off
-- Read and Write procedures for STD_ULOGIC and STD_ULOGIC_VECTOR
procedure READ(L:inout LINE; VALUE:out STD_ULOGIC);
procedure READ(L:inout LINE; VALUE:out STD_ULOGIC; GOOD: out BOOLEAN);
procedure READ(L:inout LINE; VALUE:out STD_ULOGIC_VECTOR);
procedure READ(L:inout LINE; VALUE:out STD_ULOGIC_VECTOR; GOOD: out BOOLEAN);
procedure WRITE(L:inout LINE; VALUE:in STD_ULOGIC;
JUSTIFIED:in SIDE := RIGHT; FIELD:in WIDTH := 0);
procedure WRITE(L:inout LINE; VALUE:in STD_ULOGIC_VECTOR;
JUSTIFIED:in SIDE := RIGHT; FIELD:in WIDTH := 0);
-- Read and Write procedures for STD_LOGIC_VECTOR
procedure READ(L:inout LINE; VALUE:out STD_LOGIC_VECTOR);
procedure READ(L:inout LINE; VALUE:out STD_LOGIC_VECTOR; GOOD: out BOOLEAN);
procedure WRITE(L:inout LINE; VALUE:in STD_LOGIC_VECTOR;
JUSTIFIED:in SIDE := RIGHT; FIELD:in WIDTH := 0);
--
-- Read and Write procedures for Hex and Octal values.
-- The values appear in the file as a series of characters
-- between 0-F (Hex), or 0-7 (Octal) respectively.
--
-- Hex
procedure HREAD(L:inout LINE; VALUE:out STD_ULOGIC_VECTOR);
procedure HREAD(L:inout LINE; VALUE:out STD_ULOGIC_VECTOR; GOOD: out BOOLEAN);
procedure HWRITE(L:inout LINE; VALUE:in STD_ULOGIC_VECTOR;
JUSTIFIED:in SIDE := RIGHT; FIELD:in WIDTH := 0);
procedure HREAD(L:inout LINE; VALUE:out STD_LOGIC_VECTOR);
procedure HREAD(L:inout LINE; VALUE:out STD_LOGIC_VECTOR; GOOD: out BOOLEAN);
procedure HWRITE(L:inout LINE; VALUE:in STD_LOGIC_VECTOR;
JUSTIFIED:in SIDE := RIGHT; FIELD:in WIDTH := 0);
-- Octal
procedure OREAD(L:inout LINE; VALUE:out STD_ULOGIC_VECTOR);
procedure OREAD(L:inout LINE; VALUE:out STD_ULOGIC_VECTOR; GOOD: out BOOLEAN);
procedure OWRITE(L:inout LINE; VALUE:in STD_ULOGIC_VECTOR;
JUSTIFIED:in SIDE := RIGHT; FIELD:in WIDTH := 0);
procedure OREAD(L:inout LINE; VALUE:out STD_LOGIC_VECTOR);
procedure OREAD(L:inout LINE; VALUE:out STD_LOGIC_VECTOR; GOOD: out BOOLEAN);
procedure OWRITE(L:inout LINE; VALUE:in STD_LOGIC_VECTOR;
JUSTIFIED:in SIDE := RIGHT; FIELD:in WIDTH := 0);
--synopsys synthesis_on
end STD_LOGIC_TEXTIO;
package body STD_LOGIC_TEXTIO is
--synopsys synthesis_off
-- Type and constant definitions used to map STD_ULOGIC values
-- into/from character values.
type MVL9plus is ('U', 'X', '0', '1', 'Z', 'W', 'L', 'H', '-', ERROR);
type char_indexed_by_MVL9 is array (STD_ULOGIC) of character;
type MVL9_indexed_by_char is array (character) of STD_ULOGIC;
type MVL9plus_indexed_by_char is array (character) of MVL9plus;
constant MVL9_to_char: char_indexed_by_MVL9 := "UX01ZWLH-";
constant char_to_MVL9: MVL9_indexed_by_char :=
('U' => 'U', 'X' => 'X', '0' => '0', '1' => '1', 'Z' => 'Z',
'W' => 'W', 'L' => 'L', 'H' => 'H', '-' => '-', others => 'U');
constant char_to_MVL9plus: MVL9plus_indexed_by_char :=
('U' => 'U', 'X' => 'X', '0' => '0', '1' => '1', 'Z' => 'Z',
'W' => 'W', 'L' => 'L', 'H' => 'H', '-' => '-', others => ERROR);
-- Overloaded procedures.
procedure READ(L:inout LINE; VALUE:out STD_ULOGIC; GOOD:out BOOLEAN) is
variable c: character;
variable readOk: BOOLEAN;
begin
loop -- skip white space
read(l,c,readOk); -- but also exit on a bad read
exit when ((readOk = FALSE) or ((c /= ' ') and (c /= CR) and (c /= HT)));
end loop;
if (readOk = FALSE) then
good := FALSE;
else
if (char_to_MVL9plus(c) = ERROR) then
value := 'U';
good := FALSE;
else
value := char_to_MVL9(c);
good := TRUE;
end if;
end if;
end READ;
procedure READ(L:inout LINE; VALUE:out STD_ULOGIC_VECTOR; GOOD:out BOOLEAN) is
variable m: STD_ULOGIC;
variable c: character;
variable s: string(1 to value'length-1);
variable mv: STD_ULOGIC_VECTOR(0 to value'length-1);
constant allU: STD_ULOGIC_VECTOR(0 to value'length-1)
:= (others => 'U');
variable readOk: BOOLEAN;
begin
loop -- skip white space
read(l,c,readOk);
exit when ((readOk = FALSE) or ((c /= ' ') and (c /= CR) and (c /= HT)));
end loop;
-- Bail out if there was a bad read
if (readOk = FALSE) then
good := FALSE;
return;
end if;
if (char_to_MVL9plus(c) = ERROR) then
value := allU;
good := FALSE;
return;
end if;
read(l, s, readOk);
-- Bail out if there was a bad read
if (readOk = FALSE) then
good := FALSE;
return;
end if;
for i in 1 to value'length-1 loop
if (char_to_MVL9plus(s(i)) = ERROR) then
value := allU;
good := FALSE;
return;
end if;
end loop;
mv(0) := char_to_MVL9(c);
for i in 1 to value'length-1 loop
mv(i) := char_to_MVL9(s(i));
end loop;
value := mv;
good := TRUE;
end READ;
procedure READ(L:inout LINE; VALUE:out STD_ULOGIC) is
variable c: character;
begin
loop -- skip white space
read(l,c);
exit when ((c /= ' ') and (c /= CR) and (c /= HT));
end loop;
if (char_to_MVL9plus(c) = ERROR) then
value := 'U';
assert FALSE report "READ(STD_ULOGIC) Error: Character '" &
c & "' read, expected STD_ULOGIC literal.";
else
value := char_to_MVL9(c);
end if;
end READ;
procedure READ(L:inout LINE; VALUE:out STD_ULOGIC_VECTOR) is
variable m: STD_ULOGIC;
variable c: character;
variable s: string(1 to value'length-1);
variable mv: STD_ULOGIC_VECTOR(0 to value'length-1);
constant allU: STD_ULOGIC_VECTOR(0 to value'length-1)
:= (others => 'U');
begin
loop -- skip white space
read(l,c);
exit when ((c /= ' ') and (c /= CR) and (c /= HT));
end loop;
if (char_to_MVL9plus(c) = ERROR) then
value := allU;
assert FALSE report
"READ(STD_ULOGIC_VECTOR) Error: Character '" &
c & "' read, expected STD_ULOGIC literal.";
return;
end if;
read(l, s);
for i in 1 to value'length-1 loop
if (char_to_MVL9plus(s(i)) = ERROR) then
value := allU;
assert FALSE report
"READ(STD_ULOGIC_VECTOR) Error: Character '" &
s(i) & "' read, expected STD_ULOGIC literal.";
return;
end if;
end loop;
mv(0) := char_to_MVL9(c);
for i in 1 to value'length-1 loop
mv(i) := char_to_MVL9(s(i));
end loop;
value := mv;
end READ;
procedure WRITE(L:inout LINE; VALUE:in STD_ULOGIC;
JUSTIFIED:in SIDE := RIGHT; FIELD:in WIDTH := 0) is
begin
write(l, MVL9_to_char(value), justified, field);
end WRITE;
procedure WRITE(L:inout LINE; VALUE:in STD_ULOGIC_VECTOR;
JUSTIFIED:in SIDE := RIGHT; FIELD:in WIDTH := 0) is
variable s: string(1 to value'length);
variable m: STD_ULOGIC_VECTOR(1 to value'length) := value;
begin
for i in 1 to value'length loop
s(i) := MVL9_to_char(m(i));
end loop;
write(l, s, justified, field);
end WRITE;
-- Read and Write procedures for STD_LOGIC_VECTOR
procedure READ(L:inout LINE; VALUE:out STD_LOGIC_VECTOR) is
variable tmp: STD_ULOGIC_VECTOR(VALUE'length-1 downto 0);
begin
READ(L, tmp);
VALUE := STD_LOGIC_VECTOR(tmp);
end READ;
procedure READ(L:inout LINE; VALUE:out STD_LOGIC_VECTOR; GOOD: out BOOLEAN) is
variable tmp: STD_ULOGIC_VECTOR(VALUE'length-1 downto 0);
begin
READ(L, tmp, GOOD);
VALUE := STD_LOGIC_VECTOR(tmp);
end READ;
procedure WRITE(L:inout LINE; VALUE:in STD_LOGIC_VECTOR;
JUSTIFIED:in SIDE := RIGHT; FIELD:in WIDTH := 0) is
begin
WRITE(L, STD_ULOGIC_VECTOR(VALUE), JUSTIFIED, FIELD);
end WRITE;
--
-- Hex Read and Write procedures.
--
--
-- Hex, and Octal Read and Write procedures for BIT_VECTOR
-- (these procedures are not exported, they are only used
-- by the STD_ULOGIC hex/octal reads and writes below.
--
--
procedure Char2QuadBits(C: Character;
RESULT: out std_ulogic_vector(3 downto 0);
GOOD: out Boolean;
ISSUE_ERROR: in Boolean) is
begin
case c is
when '0' => result := x"0"; good := TRUE;
when '1' => result := x"1"; good := TRUE;
when '2' => result := x"2"; good := TRUE;
when '3' => result := x"3"; good := TRUE;
when '4' => result := x"4"; good := TRUE;
when '5' => result := x"5"; good := TRUE;
when '6' => result := x"6"; good := TRUE;
when '7' => result := x"7"; good := TRUE;
when '8' => result := x"8"; good := TRUE;
when '9' => result := x"9"; good := TRUE;
when 'A' => result := x"A"; good := TRUE;
when 'B' => result := x"B"; good := TRUE;
when 'C' => result := x"C"; good := TRUE;
when 'D' => result := x"D"; good := TRUE;
when 'E' => result := x"E"; good := TRUE;
when 'F' => result := x"F"; good := TRUE;
when 'Z' => result(0) := 'Z'; result(1) := 'Z'; result(2) := 'Z'; result(3) := 'Z'; good := TRUE;
when 'X' => result(0) := 'X'; result(1) := 'X'; result(2) := 'X'; result(3) := 'X'; good := TRUE;
when 'a' => result := x"A"; good := TRUE;
when 'b' => result := x"B"; good := TRUE;
when 'c' => result := x"C"; good := TRUE;
when 'd' => result := x"D"; good := TRUE;
when 'e' => result := x"E"; good := TRUE;
when 'f' => result := x"F"; good := TRUE;
when others =>
if ISSUE_ERROR then
assert FALSE report
"HREAD Error: Read a '" & c &
"', expected a Hex character (0-F).";
end if;
good := FALSE;
end case;
end;
procedure HREAD(L:inout LINE; VALUE:out STD_ULOGIC_VECTOR) is
variable ok: boolean;
variable c: character;
constant ne: integer := value'length/4;
variable bv: std_ulogic_vector(0 to value'length-1);
variable s: string(1 to ne-1);
begin
if value'length mod 4 /= 0 then
assert FALSE report
"HREAD Error: Trying to read vector " &
"with an odd (non multiple of 4) length";
return;
end if;
loop -- skip white space
read(l,c);
exit when ((c /= ' ') and (c /= CR) and (c /= HT));
end loop;
Char2QuadBits(c, bv(0 to 3), ok, TRUE);
if not ok then
return;
end if;
read(L, s, ok);
if not ok then
assert FALSE
report "HREAD Error: Failed to read the STRING";
return;
end if;
for i in 1 to ne-1 loop
Char2QuadBits(s(i), bv(4*i to 4*i+3), ok, TRUE);
if not ok then
return;
end if;
end loop;
value := bv;
end HREAD;
procedure HREAD(L:inout LINE; VALUE:out STD_ULOGIC_VECTOR;GOOD: out BOOLEAN) is
variable ok: boolean;
variable c: character;
constant ne: integer := value'length/4;
variable bv: std_ulogic_vector(0 to value'length-1);
variable s: string(1 to ne-1);
begin
if value'length mod 4 /= 0 then
good := FALSE;
return;
end if;
loop -- skip white space
read(l,c);
exit when ((c /= ' ') and (c /= CR) and (c /= HT));
end loop;
Char2QuadBits(c, bv(0 to 3), ok, FALSE);
if not ok then
good := FALSE;
return;
end if;
read(L, s, ok);
if not ok then
good := FALSE;
return;
end if;
for i in 1 to ne-1 loop
Char2QuadBits(s(i), bv(4*i to 4*i+3), ok, FALSE);
if not ok then
good := FALSE;
return;
end if;
end loop;
good := TRUE;
value := bv;
end HREAD;
procedure HWRITE(L:inout LINE; VALUE:in std_ulogic_vector;
JUSTIFIED:in SIDE := RIGHT; FIELD:in WIDTH := 0) is
variable quad: std_ulogic_vector(0 to 3);
constant ne: integer := value'length/4;
variable bv: std_ulogic_vector(0 to value'length-1) := value;
variable s: string(1 to ne);
begin
if value'length mod 4 /= 0 then
assert FALSE report
"HWRITE Error: Trying to read vector " &
"with an odd (non multiple of 4) length";
return;
end if;
for i in 0 to ne-1 loop
quad := To_X01Z(bv(4*i to 4*i+3));
case quad is
when x"0" => s(i+1) := '0';
when x"1" => s(i+1) := '1';
when x"2" => s(i+1) := '2';
when x"3" => s(i+1) := '3';
when x"4" => s(i+1) := '4';
when x"5" => s(i+1) := '5';
when x"6" => s(i+1) := '6';
when x"7" => s(i+1) := '7';
when x"8" => s(i+1) := '8';
when x"9" => s(i+1) := '9';
when x"A" => s(i+1) := 'A';
when x"B" => s(i+1) := 'B';
when x"C" => s(i+1) := 'C';
when x"D" => s(i+1) := 'D';
when x"E" => s(i+1) := 'E';
when x"F" => s(i+1) := 'F';
when others =>
if (quad = "ZZZZ") then
s(i+1) := 'Z';
else
s(i+1) := 'X';
end if;
end case;
end loop;
write(L, s, JUSTIFIED, FIELD);
end HWRITE;
procedure Char2TriBits(C: Character;
RESULT: out bit_vector(2 downto 0);
GOOD: out Boolean;
ISSUE_ERROR: in Boolean) is
begin
case c is
when '0' => result := o"0"; good := TRUE;
when '1' => result := o"1"; good := TRUE;
when '2' => result := o"2"; good := TRUE;
when '3' => result := o"3"; good := TRUE;
when '4' => result := o"4"; good := TRUE;
when '5' => result := o"5"; good := TRUE;
when '6' => result := o"6"; good := TRUE;
when '7' => result := o"7"; good := TRUE;
when others =>
if ISSUE_ERROR then
assert FALSE report
"OREAD Error: Read a '" & c &
"', expected an Octal character (0-7).";
end if;
good := FALSE;
end case;
end;
procedure OREAD(L:inout LINE; VALUE:out BIT_VECTOR) is
variable c: character;
variable ok: boolean;
constant ne: integer := value'length/3;
variable bv: bit_vector(0 to value'length-1);
variable s: string(1 to ne-1);
begin
if value'length mod 3 /= 0 then
assert FALSE report
"OREAD Error: Trying to read vector " &
"with an odd (non multiple of 3) length";
return;
end if;
loop -- skip white space
read(l,c);
exit when ((c /= ' ') and (c /= CR) and (c /= HT));
end loop;
Char2TriBits(c, bv(0 to 2), ok, TRUE);
if not ok then
return;
end if;
read(L, s, ok);
if not ok then
assert FALSE
report "OREAD Error: Failed to read the STRING";
return;
end if;
for i in 1 to ne-1 loop
Char2TriBits(s(i), bv(3*i to 3*i+2), ok, TRUE);
if not ok then
return;
end if;
end loop;
value := bv;
end OREAD;
procedure OREAD(L:inout LINE; VALUE:out BIT_VECTOR;GOOD: out BOOLEAN) is
variable ok: boolean;
variable c: character;
constant ne: integer := value'length/3;
variable bv: bit_vector(0 to value'length-1);
variable s: string(1 to ne-1);
begin
if value'length mod 3 /= 0 then
good := FALSE;
return;
end if;
loop -- skip white space
read(l,c);
exit when ((c /= ' ') and (c /= CR) and (c /= HT));
end loop;
Char2TriBits(c, bv(0 to 2), ok, FALSE);
if not ok then
good := FALSE;
return;
end if;
read(L, s, ok);
if not ok then
good := FALSE;
return;
end if;
for i in 1 to ne-1 loop
Char2TriBits(s(i), bv(3*i to 3*i+2), ok, FALSE);
if not ok then
good := FALSE;
return;
end if;
end loop;
good := TRUE;
value := bv;
end OREAD;
procedure OWRITE(L:inout LINE; VALUE:in std_ulogic_vector;
JUSTIFIED:in SIDE := RIGHT; FIELD:in WIDTH := 0) is
variable tri: std_ulogic_vector(0 to 2);
constant ne: integer := value'length/3;
variable bv: std_ulogic_vector(0 to value'length-1) := value;
variable s: string(1 to ne);
begin
if value'length mod 3 /= 0 then
assert FALSE report
"OWRITE Error: Trying to read vector " &
"with an odd (non multiple of 3) length";
return;
end if;
for i in 0 to ne-1 loop
tri := To_X01Z(bv(3*i to 3*i+2));
case tri is
when o"0" => s(i+1) := '0';
when o"1" => s(i+1) := '1';
when o"2" => s(i+1) := '2';
when o"3" => s(i+1) := '3';
when o"4" => s(i+1) := '4';
when o"5" => s(i+1) := '5';
when o"6" => s(i+1) := '6';
when o"7" => s(i+1) := '7';
when others =>
if (tri = "ZZZ") then
s(i+1) := 'Z';
else
s(i+1) := 'X';
end if;
end case;
end loop;
write(L, s, JUSTIFIED, FIELD);
end OWRITE;
-- Hex Read and Write procedures for STD_LOGIC_VECTOR
procedure HREAD(L:inout LINE; VALUE:out BIT_VECTOR;GOOD:out BOOLEAN) is
variable tmp: std_ulogic_vector(VALUE'length-1 downto 0);
begin
HREAD(L, tmp, GOOD);
VALUE := To_BitVector(tmp);
end HREAD;
procedure HREAD(L:inout LINE; VALUE:out BIT_VECTOR) is
variable tmp: std_ulogic_vector(VALUE'length-1 downto 0);
begin
HREAD(L, tmp);
VALUE := To_BitVector(tmp);
end HREAD;
-- Hex Read and Write procedures for STD_LOGIC_VECTOR
procedure HREAD(L:inout LINE; VALUE:out STD_LOGIC_VECTOR) is
variable tmp: STD_ULOGIC_VECTOR(VALUE'length-1 downto 0);
begin
HREAD(L, tmp);
VALUE := STD_LOGIC_VECTOR(tmp);
end HREAD;
procedure HREAD(L:inout LINE; VALUE:out STD_LOGIC_VECTOR; GOOD: out BOOLEAN) is
variable tmp: STD_ULOGIC_VECTOR(VALUE'length-1 downto 0);
begin
HREAD(L, tmp, GOOD);
VALUE := STD_LOGIC_VECTOR(tmp);
end HREAD;
procedure HWRITE(L:inout LINE; VALUE:in STD_LOGIC_VECTOR;
JUSTIFIED:in SIDE := RIGHT; FIELD:in WIDTH := 0) is
begin
HWRITE(L, STD_ULOGIC_VECTOR(VALUE), JUSTIFIED, FIELD);
end HWRITE;
-- Octal Read and Write procedures for STD_ULOGIC_VECTOR
procedure OREAD(L:inout LINE; VALUE:out STD_ULOGIC_VECTOR;GOOD:out BOOLEAN) is
variable tmp: bit_vector(VALUE'length-1 downto 0);
begin
OREAD(L, tmp, GOOD);
VALUE := To_X01(tmp);
end OREAD;
procedure OREAD(L:inout LINE; VALUE:out STD_ULOGIC_VECTOR) is
variable tmp: bit_vector(VALUE'length-1 downto 0);
begin
OREAD(L, tmp);
VALUE := To_X01(tmp);
end OREAD;
-- Octal Read and Write procedures for STD_LOGIC_VECTOR
procedure OREAD(L:inout LINE; VALUE:out STD_LOGIC_VECTOR) is
variable tmp: STD_ULOGIC_VECTOR(VALUE'length-1 downto 0);
begin
OREAD(L, tmp);
VALUE := STD_LOGIC_VECTOR(tmp);
end OREAD;
procedure OREAD(L:inout LINE; VALUE:out STD_LOGIC_VECTOR; GOOD: out BOOLEAN) is
variable tmp: STD_ULOGIC_VECTOR(VALUE'length-1 downto 0);
begin
OREAD(L, tmp, GOOD);
VALUE := STD_LOGIC_VECTOR(tmp);
end OREAD;
procedure OWRITE(L:inout LINE; VALUE:in STD_LOGIC_VECTOR;
JUSTIFIED:in SIDE := RIGHT; FIELD:in WIDTH := 0) is
begin
OWRITE(L, STD_ULOGIC_VECTOR(VALUE), JUSTIFIED, FIELD);
end OWRITE;
--synopsys synthesis_on
end STD_LOGIC_TEXTIO;
Sie muss mit vcim 2002 kompiliert werden.